Ch.1-2 Hemocytometer - counting cells manually
- NanoEntek

- May 16, 2022
- 2 min read
Updated: Aug 1, 2022
Previous blog post briefly covered the introduction of hemocytometer. In this post, the followings will be covered:
- when do you use hemocytometer?
- how do you use hemocytometer?
- tips for counting cells with hemocytometer
When do you use hemocytometer?
For those who count cells manually, a hemocytometer should be very familiar instrument you work with. It is the standard manual cell counting technique.
For those who prefer cheaper and non-electronic device, hemocytometer is the best option.
So how do you use hemocytometer?
To use a hemocytometer, you need to prepare few materials.
You will need:
Prepared cell sample
A coverslip for hemocytometer
A pipette and tips
Trypan blue staining solution
A tally counter
A microscope
Simple cell counting procedure using the NI chamber is as follows:
1. Clean a hemocytometer and coverslip with alcohol.
2. Place the coverslip on the hemocytometer.
3. Pipette 10 μL of sample stained with trypan blue into the chamber.
4. Place the hemocytometer on the microscope stage for counting.
5. Start counting at the upper left square.
Manual counting method
Once cells have been stained with trypan blue, they are then loaded into the hemocytometer chamber. When counting, you do NOT need to count all cells in every square. Instead, count the cells in four corner squares and those on two sides of square such as top and left or left and bottom lines.
Tips for counting with hemocytometer

Tip 1: It is easier to count in zigzag pattern by starting from the upper left square.
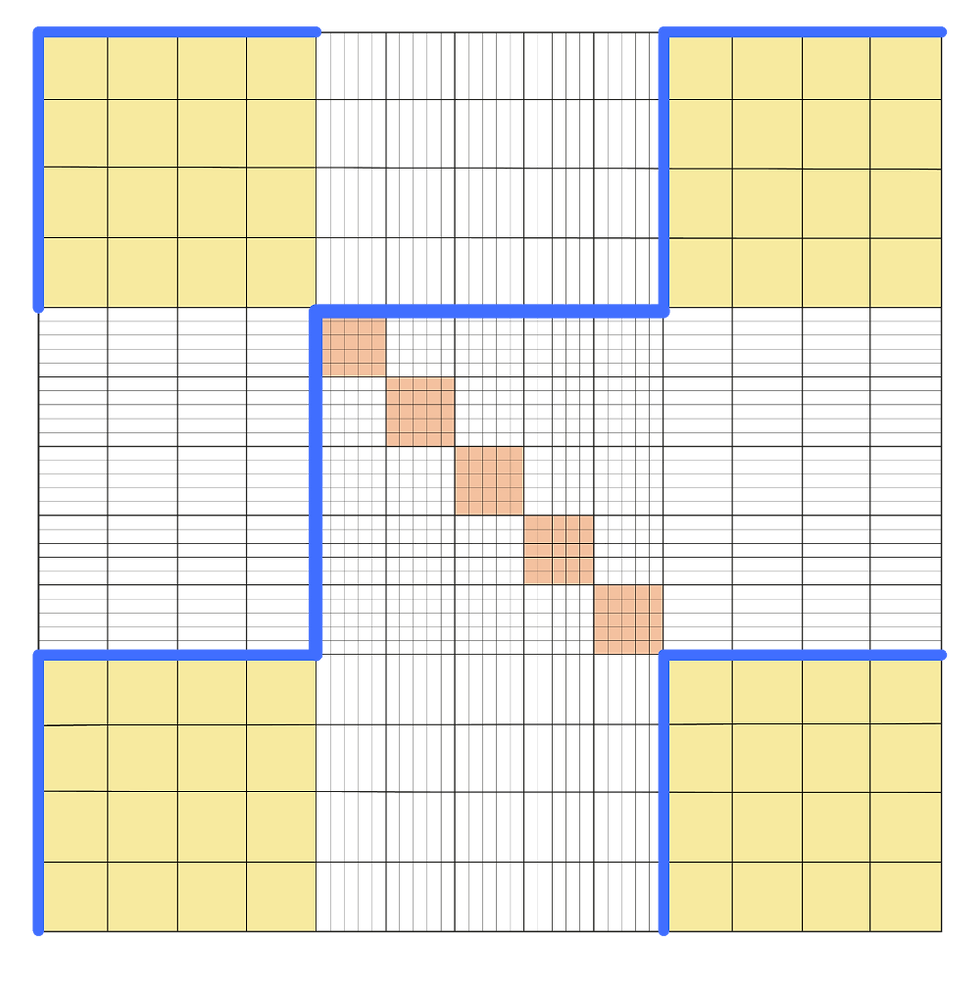
Tip 2: Only count cells that are on the upper and left grid of the square.
Trypan blue staining

When counting cells using hemocytometer, we need something called trypan blue staining solution to distinguish live (viable) from dead (non-viable) cells. Trypan blue is an azo dye that stains dead cells all blue whereas live cells remain clear.
Once diluting your sample with trypan blue, simply place it on a microscope and count.
Ever since the development of hemocytometer, the method of cell counting has been improving for better and easier use. The hemocytometer is still widely used due to its simplicity and cost efficiency.
Today, you not only have manual but also automated cell counter as your option. Choosing the right product for your cell counting really depends on your preference and your circumstances so it is recommended to take some time to consider your best fit.
For users who still prefer manual counting, materials used for manual counting such as counting slides are advancing as well. Back in the days, only reusable glass hemocytometer was used but disposable plastic slide is now available and mostly used in consideration of safety and time.
Choose what suits you best and count away!
[C-chip (4ch)]
Disposable hemocytometer

Specifications
Cat. No. | Grid | Chamber depth (um) | Loading volume (uL) |
|---|---|---|---|
DHC-N04 | Neubauer Improved (NI) | 100 | 10 |
DHC-B04 | Burker Turk (BT) | 100 | 10 |
DHC-F04 | Fuchs Rosenthal (FR) | 200 | 20 |
No cover slip | No washing | No exposure to hazardous materials
[C-chip (2ch)]
Disposable hemocytometer

Specifications
Cat. No. | Grid | Chamber depth (um) | Loading volume (uL) |
|---|---|---|---|
DHC-N01 | Neubauer Improved (NI) | 100 | 10 |
DHC-B01 | Burker (B) | 100 | 10 |
DHC-B02 | Burker Turk (BT) | 100 | 10 |
DHC-F01 | Fuchs Rosenthal (FR) | 200 | 20 |
DHC-M01 | Malassez (MA) | 200 | 20 |
No cover slip | No washing | No exposure to hazardous materials
Applicable for Blood analysis & cell counting (viability) | Cell culture | Microbiology
[S-chip]
Disposable cell counting chamber

Specifications
Cat. No. | Grid | Chamber depth (um) | Loading volume (uL) |
|---|---|---|---|
DCS-S01 | Negative | 20 | 2 to 3 |
No cover slip | No washing | No exposure to hazardous materials
Applicable for Sperm counting
References:
1.“Definition of HEMACYTOMETER.” www.merriam-Webster.com, www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/hemacytometer. Accessed 24 Feb. 2022.
2. Liu, Shijie. “How Cells Grow.” Bioprocess Engineering, 2017, pp. 629–697, www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780444637833000113, 10.1016/b978-0-444-63783-3.00011-3. Fuentes, Maria. “Hemocytometer Square Size • Hemocytometer.” Hemocytometer, 11 Apr. 2013, www.hemocytometer.org/hemocytometer-square-size/.
4. “Cell Counting with a Hemocytometer | the Privalsky Lab @ UCDavis.” Ucdavis.edu, 2019, microbiology.ucdavis.edu/privalsky/hemocytometer.
5. Mahak Jalan. “What Is a Hemocytometer?” Science ABC, Science ABC, 16 Aug. 2017, www.scienceabc.com/pure-sciences/what-is-a-hemocytometer-calculation-counting-how-to-use.html.





Comments